Will Generative AI solve all software adoption challenges?

Table of Contents
Software adoption: A road with many speed bumps
Imagine you’re navigating a labyrinth. Each wrong turn costs you time and resources – that’s what issues with software adoption can feel like. Companies bump into several obstacles like user resistance, which can stem from a lack of understanding of new software.
Therefore, software adoption is an essential element of any digital transformation initiative. It requires employees to acquire the skills and knowledge necessary to use new software or technology correctly. It is up to organizations to ensure that users are able to successfully adopt new software so that digital transformation initiatives can reach their full potential.
By providing a seamless user experience, companies can reduce digital friction, which in turn leads to increased productivity and better overall results from their technology investments.
Additionally, companies should measure the impact of these efforts so they can adjust their strategy if needed.

Unpacking Generative AI: The ‘techy bit’
Generative AI works by analyzing large datasets and generating patterns which it then uses to create new information. It can learn complex relationships between different elements within a dataset, enabling it to generate realistic-looking images or text that are based on the original training data. For example, generative AI can be used to create virtual humans with facial expressions that appear realistic but have never before existed in any form other than computer code.
The power of generative AI lies in its ability to understand the underlying structure of the data it works with: for instance, when it processes an image, it not only recognizes objects but also learns how they are connected in order for the image to make sense visually.
Technically speaking, generative AI uses deep learning models to understand patterns and context within the data it has been trained on. Using neural networks with multiple layers, it can make sense of intricate details that simpler algorithms overlook. One of its notable strengths is in natural language processing (NLP), where it excels at understanding the nuances and complexities of human language. This capability makes it particularly useful in areas such as chat support, data analytics, and problem-solving.
The promise of Generative AI in software adoption
Generative AI can help organizations achieve better software adoption rates. Here are a few examples:
- Automate user support tasks
- Identify user behavior patterns
- Analyze user feedback in real-time
- Uncover correlations between different behaviors and outcomes
- Analyze user behavior to identify user points of friction
- Create support scripts from existing support conversations
However, when imagining generative AI in the context of software adoption, most users are thinking of chat interfaces like ChatGPT, and asking it to complete tasks in any application. Unfortunately, reality is not that simple.
Limitations: One size does not fit all
While generative AI offers intriguing possibilities, it’s not a silver bullet – there are several factors limiting the use of generative AI for software adoption in large enterprises:
- Small datasets due to specific processes
GenAI might not understand the company’s individual processes and workflows in particular applications like Salesforce, Workday, SAP, or Oracle, which are configured to each organization’s specific needs. Primarily, generative AI models require large datasets to be effective; if the data is too small or inaccurate, errors may occur. Organizations with a large long tail of smaller applications will struggle to gather the necessary data for a meaningful GenAI use case. - Biased models
Bias can be introduced into an AI model if the data used for training is biased. This means that the output generated by generative AI models could be skewed and inaccurate. This lack of nuance could result in solutions that, although technically sound, are not practical or palatable for specific organizational contexts. - Data quality
Another important point to note is that the efficacy of generative AI depends on the quality of the data it is trained on. Inadequate or incorrect data can significantly hamper its performance, and as people struggle to operate complex software, using wrong or incomplete data in powerful AI applications can cause serious damage to a business. - Dealing with change
Finally, generative AI models are trained on a set of conditions that may no longer apply in changing scenarios. This means that generative AI models may not always be able to adapt to new circumstances and produce accurate results. For example, if a process changes over time, the AI model might not be able to detect this and produce results accordingly.
These limitations must be taken into consideration when leveraging generative AI for software adoption initiatives. Companies should ensure that they have sufficient data for training their generative AI models and that any potential biases are addressed. Having realistic expectations about what can and cannot be achieved with this technology is key to ensuring success when using it for software adoption initiatives.
How a Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) can help
Organizations looking to utilize the power of AI must consider how they will collect the necessary data for analysis.
Digital adoption platforms (DAPs) are incredibly helpful here as they enable organizations to track user behaviors automatically and identify areas where software adoption can be improved upon without having their own development team involved.
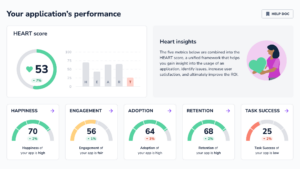
Data accuracy and quantity are essential components for the successful implementation of AI technologies within an organization; this means investing time into collecting quality datasets as well as identifying areas where bias might exist so that all outputs from the model are unbiased and reliable.
In addition to that, a Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) is a powerful tool that can help organizations reduce digital friction and increase software adoption rates. By providing users with personalized guidance and support, DAPs make using complex software applications easier and more efficient.
DAPs are also easy to deploy and integrate into existing software applications without requiring extensive investments in training or development resources.
By leveraging the power of generative AI combined with a Digital Adoption Platform such as Userlane’s solution, businesses can gain valuable insights into how digital transformation initiatives are progressing and make adjustments as needed by creating personalized user experiences that ensure successful outcomes from their technology initiatives.
Userlane has taken a unique approach by incorporating generative AI functionalities into its platform. This creates a balanced, symbiotic relationship. While generative AI provides fast, automated solutions, Userlane ensures these solutions are effectively implemented and truly resonate with what the organization needs.
This dual approach ensures a more comprehensive, nuanced, and effective strategy for overcoming software adoption challenges. Also, Userlane’s strategic partnership with Microsoft leverages OpenAI’s technology to provide a platform that understands your company’s specific pain points and complements that with the quick and scalable solutions that generative AI can offer.
Conclusion: The holistic approach to software adoption
While generative AI offers a wealth of advantages, it’s not the be-all and end-all solution for software adoption challenges. When combined with a robust, intuitive, and scalable Digital Adoption Platform like Userlane, you’re arming your organization with an unmatched set of tools. Together, they ensure that you not only navigate the adoption challenges effectively but also realize the full potential of your technology investments.

